JAX-RS @Produces with Example – RESTful Web Services Tutorial
7 years ago Lalit Bhagtani 0
In JAX-RS @Produces annotation is used to specify the MIME media type ( output ) that a resource method can produce and send it back to the client.
@Produces annotation can be applied at both class level and method level. If it is applied at the class level, all the methods in a resource will produce the specified MIME type by default and if it is applied at the method level, then annotated method will produce the specified MIME type by overriding any @Produces annotations applied at the class level.
If any method in a resource is not able to produce the specified MIME type, then Jersey runtime sends back an HTTP “406 Not Acceptable” error to the client.
The value of @Produces annotation is an array of String of MIME types. For example:
@Produces(MediaType.TEXT_PLAIN)
@Produces(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON)
@Produces(MediaType.APPLICATION_XML)
Let’s try to understand it with an example.
Example 1 :-
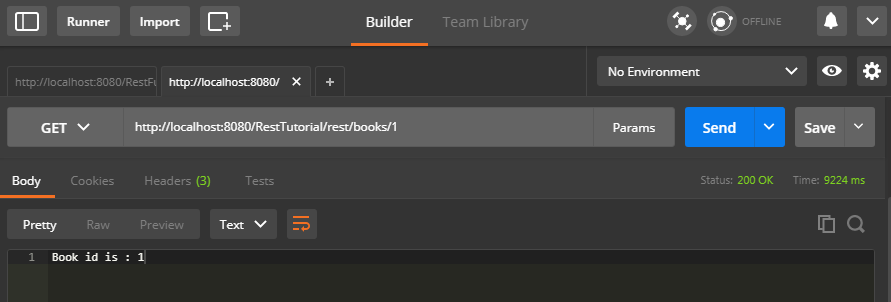
In this example of JAX-RS @Produces, we will hit this URL <base URL>/books/1 with HTTP GET method to get the book resource of id 1 in plain text format.
import javax.ws.rs.GET;
import javax.ws.rs.Path;
import javax.ws.rs.PathParam;
import javax.ws.rs.Produces;
import javax.ws.rs.core.MediaType;
import javax.ws.rs.core.Response;
@Path("books")
public class ProducesAnnotationExample {
@GET
@Produces(MediaType.TEXT_PLAIN)
@Path("/{id}")
public Response getAllBooks(@PathParam("id") String bookId){
return Response.status(200)
.entity("Book id is : " + bookId).build();
}
}
Result :-
Example 2 :-
Book.java
Create a bean class “Book” with few class members. This class will be used as an entity to send a response to client in JSON format. We also annotated our bean class with @XmlRootElement marking it as a root element, so that we can use same bean class to send a response to client in XML format.
import javax.xml.bind.annotation.XmlRootElement;
@XmlRootElement
public class Book {
private String id;
private String name;
private String authorName;
private int volumeNumber;
public String getId() {
return id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getAuthorName() {
return authorName;
}
public void setAuthorName(String authorName) {
this.authorName = authorName;
}
public int getVolumeNumber() {
return volumeNumber;
}
public void setVolumeNumber(int volumeNumber) {
this.volumeNumber = volumeNumber;
}
}
Dependency
Add one dependency in pom file of your project. This dependency is required by jersey library to convert your bean class in to JSON format and vice versa.
<dependency>
<groupId>org.glassfish.jersey.media</groupId>
<artifactId>jersey-media-moxy</artifactId>
<version>2.26-b03</version>
</dependency>
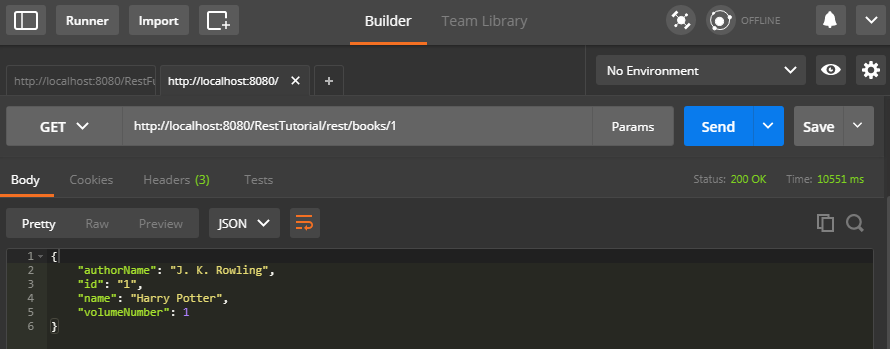
In this example of JAX-RS @Produces, we will hit this URL <base URL>/books/1 to get the book resource of id 1 in JSON format.
import javax.ws.rs.GET;
import javax.ws.rs.Path;
import javax.ws.rs.PathParam;
import javax.ws.rs.Produces;
import javax.ws.rs.core.MediaType;
import javax.ws.rs.core.Response;
@Path("books")
public class ProducesAnnotationExample {
@GET
@Produces(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON)
@Path("/{id}")
public Response getAllBooks(@PathParam("id") String bookId){
Book book = new Book();
book.setId(bookId);
book.setName("Harry Potter");
book.setVolumeNumber(1);
book.setAuthorName("J. K. Rowling");
return Response.status(200)
.entity(book).build();
}
}
Result :-
Example 3 :-
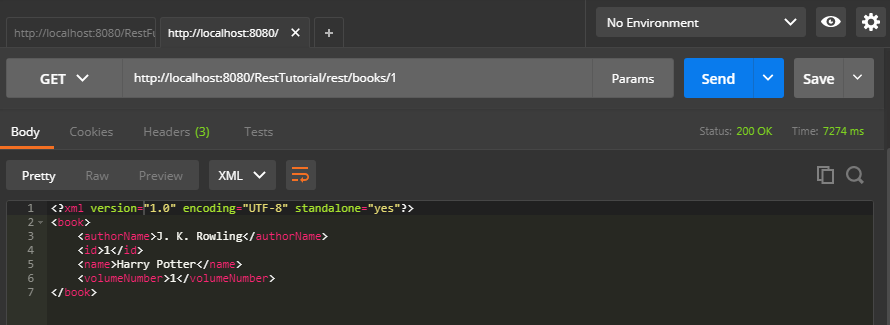
In this example of JAX-RS @Produces, we will hit this URL <base URL>/books/1 to get the book resource of id 1 in XML format.
import javax.ws.rs.GET;
import javax.ws.rs.Path;
import javax.ws.rs.PathParam;
import javax.ws.rs.Produces;
import javax.ws.rs.core.MediaType;
import javax.ws.rs.core.Response;
@Path("books")
public class ProducesAnnotationExample {
@GET
@Produces(MediaType.APPLICATION_XML)
@Path("/{id}")
public Response getAllBooks(@PathParam("id") String bookId){
Book book = new Book();
book.setId(bookId);
book.setName("Harry Potter");
book.setVolumeNumber(1);
book.setAuthorName("J. K. Rowling");
return Response.status(200)
.entity(book).build();
}
}
Result :-
References :-
That’s all for JAX-RS @Produces with Example. If you liked it, please share your thoughts in comments section and share it with others too.
